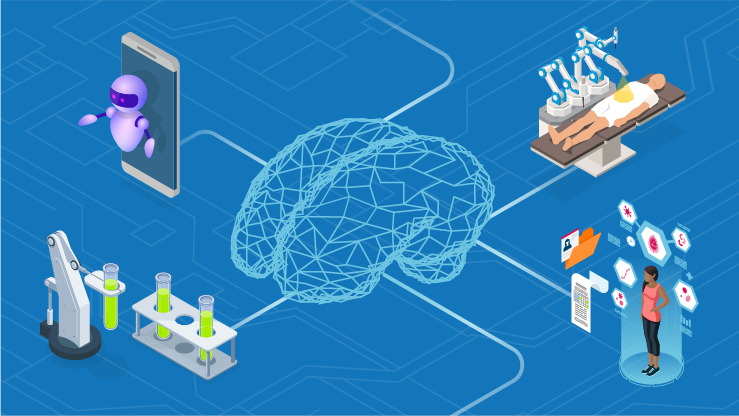
The narrative has moved on. It used to be that AI brought fear into the minds of medical staff and patients, driven by uncertainty over whether AI will replace jobs as well as its impact on tools and services. But as healthcare increasingly incorporates AI innovations into its ways of working, it’s clear these tools aren’t here to replace humans; they’re here to assist them.
At the same time, the growing reliance on AI is surfacing new risks. Here are four ways medical staff are using AI tools to deliver better quality care, and the risks they must address to work safely and with confidence.
-
Remote care and monitoring
An age-old catch-22 is that many people who need healthcare lack the mobility to get to a hospital. Thankfully, AI-driven tools are making remote care possible. Today, patients can access a variety of specialized care in their own homes via telehealth, cutting the number hospital visits and shortening wait times. AI is also being used to monitor patients remotely, with tools like pulse oximeters and weighing scales feeding data back to medical staff.
The downside to remote care and monitoring is it depends on digital devices which aren’t immune from errors. A faulty device could result in injury or a condition worsening, with the omnipresent threat of cyber attacks also leaving patient data at risk. By getting cover for AI and any devices it works through, you’ll be protected if a device fails or if a cyber event hits.
-
Accurate diagnosis
Health data is vital in quickly and accurately diagnosing patient conditions, but it’s a mammoth task for human workers to analyse. AI is showing how it can complete this task with remarkable speed and accuracy, to ultimately improve decision making. For example, in the US an AI tool is reviewing and translating mammograms 30 times faster than human doctors and with 99% accuracy, cutting out human errors and reducing the need for unnecessary biopsies.
AI is only as good as the information that’s put in. If the data set lacks quality, the sample size is too small or unrepresentative, a human error is made during input or an error in the AI’s code is missed, it can result in errors and misdiagnosis. And if things do go wrong, who is responsible, the AI tool or the human? When the cause is ambiguous, having the right bodily injury cover is vital in removing any liability confusion.
-
Medical research
Typically, it takes years for new medicines to pass through the different stages of research, discovery and testing to reach the patient. AI tools can rapidly accelerate this process, using their vast computing power to collect data in a way that enhances recruitment and data analysis in clinical trials, and to complete reports and intelligently interpret data. The result is a more streamlined process that cuts costs for the medical organization while getting potentially life-changing treatments to patients faster.
We’ve already touched on how AI relies on information that is input. What if a human error or system fault occurs during medical research, leading to a medicine that is in some way harmful being produced and distributed? That’s a serious bodily injury exposure. If the medicine is recalled, it can also result in loss of income for the supplier, along with significant business interruption loss. It’s vital that researchers, producers and distributors all cover themselves against these risks.
-
Automated tasks
Many people enter the field of healthcare simply to help people. But medical staff often have mountains of administrative tasks to work through, restricting their time with patients. Add in the fact departments often find themselves short-staffed, and the workload can lead to burnout. Here, AI tools are a gamechanger, freeing medical staff from their administrative burdens by taking on manual tasks that can be automated, like virtual scribes, maintaining records, scan analysis and data entry. Not only does this reduce costs and improve efficiencies, but it also helps relieve staff stress and creates more time for treating patients.
The more reliant healthcare becomes on AI to complete tasks, the greater the risk of operational disruption if downtime occurs. Technology failure or a cyber event can impact patient care and cause financial loss, so it pays to allow breathing room for financial loss in your insurance policy.
How can medical staff maximize the AI opportunity?
AI is not just transforming healthcare at a clinical level; it’s transforming how the entire industry works. Medical staff are embracing the technology, and rightly so. But at the same time, AI introduces new exposures that must be addressed, from the question of who is liable if AI fails or makes an error, to the growing threat of cybercrime.
Fully depending on the technology is risky business. To maximize it’s potential, it’s vital to retain human input and ensure the right insurance cover is in place.
Ready to talk AI and healthcare? Reach out to our expert team with any questions. We’d love to hear from you.